33-year-old G1 P0 at 39 weeks with a history gestational diabetes presents in labor. After delivering the head you see it retract slightly (turtle sign). On the next push you are unable to delivery the anterior shoulder with gentle downward traction.
Shoulder dystocia typically occurs when the anterior shoulder impacts on the pubic symphysis, less often when posterior shoulder impacts on the sacral promontory. Risk factors include abnormal maternal pelvic anatomy, gestational diabetes, post-dates pregnancy, previous shoulder dystocia, short maternal stature, and fetal macrosomia.
How do you manage this difficult case?
HELPERR Mnemonic1,2
Help – Call for help – OB, neonatology, and anesthesia
Empty bladder – Catheterize to increase AP diameter
- Classically episiotomy however only consider if needing additional room for internal maneuvers (Rubin, Woods, Barnum)
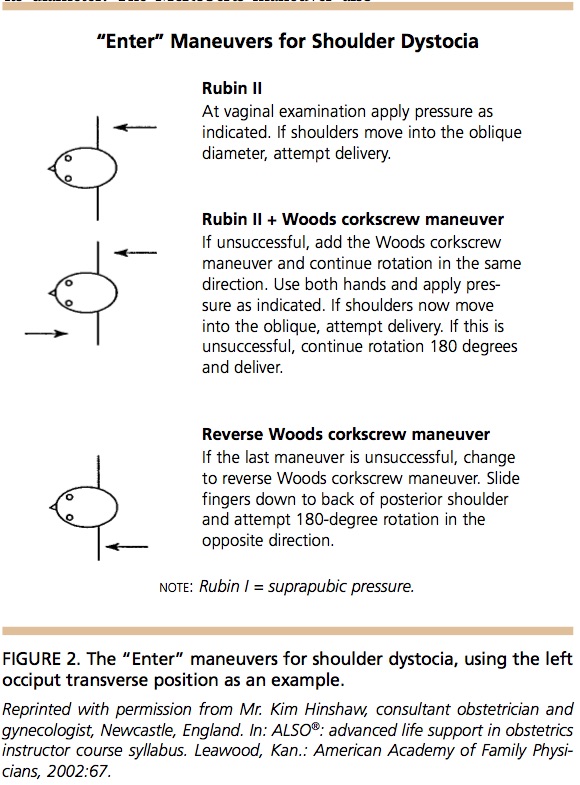
Legs flexed – McRoberts maneuver
- Place mother in lithotomy position (supine with buttocks at edge of the bed)
- Hyperflex and abduct the hips by placing the knees against the lateral abdomen
Pressure – Suprapubic to dislodge anterior shoulder
- Apply suprapubic pressure downward with palm or fist
- 30 seconds of continuous pressure
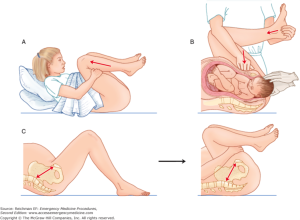
Enter vagina – Rubin or Woods corkscrew maneuver2
- Rubin Maneuver
- Insert fingers of hand behind the posterior aspect of the anterior shoulder and rotate shoulder toward fetal chest
- Woods Corkscrew maneuver
- Insert two fingers on anterior aspect of posterior shoulder
- Pressure applied to rotate it posterolaterally
- If is shoulder is oblique attempt delivery
- If unsuccessful continue to rotate 180 degrees
- May combine maneuvers to increase rotation, may be limited secondary to space and patient tolerance
Remove posterior arm – Barnum maneuver2
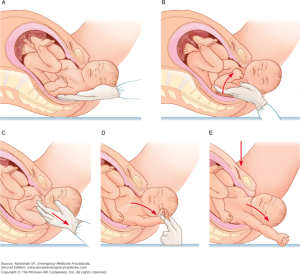
- Insert hand into vagina on posterior aspect of posterior arm/humerus
- Deliver the posterior arm by sweeping the fetal arm over the anterior chest wall
- Deliver the posterior arm/shoulder
- Apply gentle downward traction of the fetal head/arm to facilitate delivery
Roll – Gaskin maneuver
- Position patient on all-fours
- Deliver fetus by gentle downward pressure on posterior shoulder or upward traction on anterior shoulder
- May be better tolerated than Rubin, Wood, or Barnum maneuvers
Maneuvers of last resort2
- Fracture of the fetal clavicle – midpoint of clavicle and exert pressure outward (away from the lung) rapidly
- Symphysiotomy3
- Zavanelli maneuver – cephalic replacement into the birth canal followed by cesarean delivery
References/Further Reading1,4
- Baxley EG, Gobbo RW. Shoulder dystocia. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69(7):1707-1714.
- Reichman EF. Chapter 133. Shoulder Dystocia Management. Emergency Medicine Procedures, 2e. New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2013.
- Reichman EF. Chapter 137. Symphysiotomy. Emergency Medicine Procedures, 2e. New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2013. Available at: http://accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?sectionid=45343778&bookid=683&jumpsectionID=45354637&Resultclick=2 Accessed: January 13, 2017
- Linker J. The Complicated Delivery: What Do You Do? emDocs 2016. Accessed Jan 13, 2017.