Have you ever tried to figure out what the appropriate starting dose of naloxone is? When you dig in the literature it’s pretty clear that its a lot of hand waving and muddy water — but let me give you an approach and some of the literate that is out there
Apneic patient: 1-2mg naloxone
Altered with respiratory depression: 0.1 mg and repeat with increasing doses* every 2 minutes with close monitoring for response
Goal: sleepy, but with adequate respirations
Duration of action: 30-45 minutes (most patients need repeat dosing or a drip)
How to make a drip?
- Calculate the dose the patient required for response, for example 1mg.
- Then reduce to 2/3 (0.6 mg) because you would like to keep them breathing but sleepy and not alert and agitated
- Give that amount (2/3 of response dose or in our example 0.6) over 1 hour
*A recent article on initial naloxone doses / titration
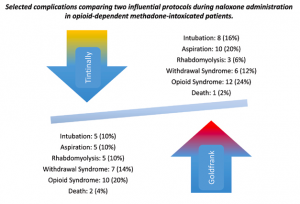
included one-hundred opioid-dependent patients with signs/symptoms of methadone overdose. Patients were split in to 2 groups. Group 1 received naloxone with the dose 0.1 mg given every two to three minutes while group 2 received naloxone with the initial dose of 0.04 mg increasing to 0.4, 2, and 10 mg every two to three minutes to reverse respiratory depression. The time to reversal of the overdose signs/symptoms was significantly less in group 2 (P<0.001). Frequency of withdrawal syndrome and recurrence of respiratory depression were not significantly different between the two groups.
So, the jury is still out, but I hope this gives you a sense of the options out there and clarifies some of the nebulous answer provided by UTD.
References:
Berlot G et al. Naloxone in cardiorespiratory arrest. Anaesthesia. 1985;40(8):819.
https://www-uptodate-com.eresources.mssm.edu/contents/naloxone-drug-information?search=naloxone&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~149&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
https://www-uptodate-com.eresources.mssm.edu/contents/acute-opioid-intoxication-in-adults?search=opioid%20overdose&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#H13
Goldfrank L, et al. A dosing nomogram for continuous infusion intravenous naloxone. Ann Emerg Med. 1986 May;15(5):566-70.
Khosravi N, et al. Comparison of Two Naloxone Regimens in Opioid-dependent Methadone overdosed Patients: A Clinical Trial Study. Current Clinical Pharmacology. Vol 12 :4 . 2017.