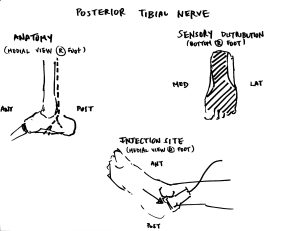
Today’s lower extremity block is going to be the posterior tibial nerve. The sensory distribution should be helpful for things like foreign bodies that need to be taken out of the foot.
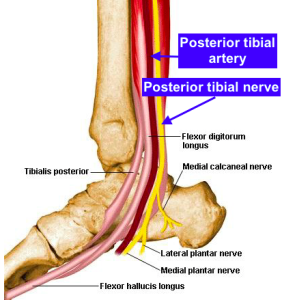
 Anatomy – The largest of the five nerves at the level of the ankle, the posterior tibial nerve is posterior to the posterior tibial artery (labeled in the above figure). Detailed on the NYSORA website, the tendons in the area (e.g., tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus tendons, and flexor hallucis longus) can appear quite similar to the nerve; however, the nerve runs in close proximity to the artery.
Anatomy – The largest of the five nerves at the level of the ankle, the posterior tibial nerve is posterior to the posterior tibial artery (labeled in the above figure). Detailed on the NYSORA website, the tendons in the area (e.g., tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus tendons, and flexor hallucis longus) can appear quite similar to the nerve; however, the nerve runs in close proximity to the artery.
Sensory distribution – Heel and sole of the foot. Depicted in the figure above by the cross-hatched area.
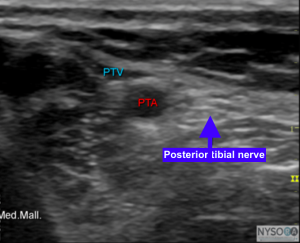
Injection site – As depicted in the figure above, the injection site can be identified using the linear transducer. The ultrasound probe is placed at the level of the medial malleolus and the posterior tibial nerve can be located just posterior to the artery.
References
http://www.nysora.com/techniques/ultrasound-guided-techniques/lower-extremity/3073-ultrasound-guided-ankle-block.html