Clinical Scenario:
A 68-year-old man with a past medical history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and recent admission for pneumonia presents with fever and diarrhea for 5 days. The patient has had multiple watery stools per day. Associated symptoms include mild vague abdominal pain but no nausea or vomiting. Exam is notable for mild diffuse abdominal tenderness but no rebound or guarding. You send stool studies and he is clostridium difficile positive. He is started on oral flagyl and admitted. Does this patient require imaging?
Imaging in Clostridium difficile
Routine use of imaging in C. difficile is not necessary for the diagnosis or management of mild to moderate C. diff. Findings on CT scan may include non-specific colonic wall thickening. Indications for imaging include severe C. diff or suspicion for complications such as toxic megacolon or colonic perforation.1 The risk of developing a complication (toxic megacolon, perforation, colectomy, or shock) is 11%.2 Risk factors for severe C. diff and its complications are age >80 years, underlying medical comorbidities (chronic heart, lung, or kidney disease), renal failure, and high white blood cell count (≥ 20).2 Below is a brief overview of severe C. diff, toxic megacolon, and colonic perforation to aid in decision making about imaging.
Severe C. diff colitis
- Profuse diarrhea (≥ 6 stools/day), abdominal pain, fever, marked leukocytosis (WBC count > 20,000/uL, and azotemia1
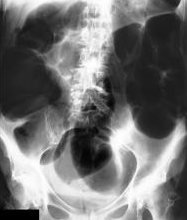
Toxic megacolon is defined as transverse/ascending colon dilation of ≥ 6cm on plain X-ray in acute colitis and clinical criteria (systemic signs of toxicity):3
1 of 3: fever > 101.5 F, heart rate > 120bpm, or WBC > 10.5/anemia
-AND-
1 of 4: dehydration, mental changes, electrolyte disturbance, or hypotension
Signs and Symptoms include: abdominal distension, extreme abdominal tenderness (be wary in patients with altered mental status), constipation, obstipation, and reduced bowel sounds.
Colonic Perforation signs and symptoms include: abdominal pain, sudden worsening of pain with dissipation, abdominal distension, peritonitis
Take Home Points
- Obtain imaging in severe C. diff colitis
- Obtain imaging if the person has significant abdominal pain or tenderness
- Keep in mind toxic megacolon and colonic perforation
References
- Pant C, Sferra TJ, Deshpande A, Minocha A. Clinical approach to severe Clostridium difficile infection: update for the hospital practitioner. Eur J Intern Med. 2011;22(6):561-568.
- Abou Chakra CN, McGeer A, Labbe AC, et al. Factors Associated With Complications of Clostridium difficile Infection in a Multicenter Prospective Cohort. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61(12):1781-1788.
- Gan SI, Beck PL. A new look at toxic megacolon: an update and review of incidence, etiology, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(11):2363-2371.