Introduction:
Bedside cardiac ultrasound is useful in the setting of trauma as well as medical illness. The most basic assessments of cardiac activity (or standstill) and the presence of pericardial fluid or tamponade can be made rapidly and alter patient management. Advanced cardiac ultrasound assessments can include a rough estimation of global cardiac contractility (normal vs. hypocontractile), or incorporation of ultrasound into ACLS algorithms (to confirm asystole or detect a possible cause for PEA).
Focused Questions:
- Is there cardiac activity?
- Is there a pericardial effusion?
Video Overview:
Required Views:
At least two views are required, taken from the following possible views.
1. Subxiphoid Four-Chamber View
| Probe position | Image |
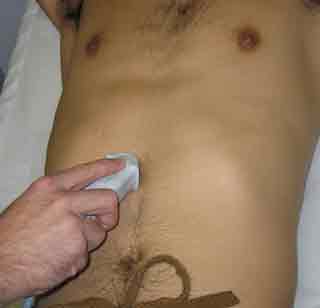 |
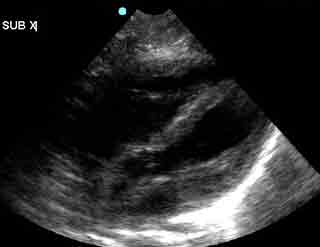 |
| Notes | |
|
|
| Abnormal Studies | |
 |
|
2. Parasternal Long Axis View
| Probe position | Image |
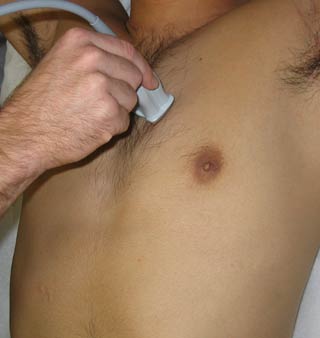 |
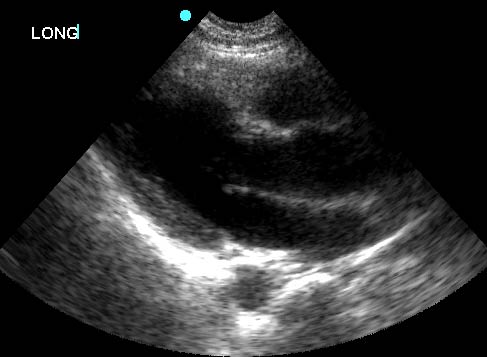 |
| Notes | |
|
|
3. Parasternal Short Axis View
| Probe position | Image |
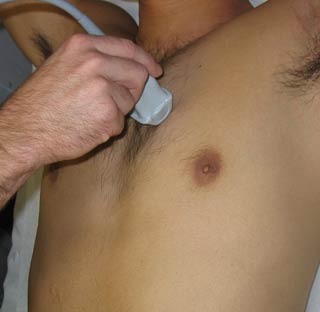 |
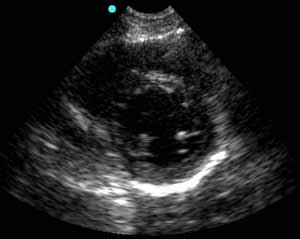 |
| Notes | |
|
|
| Abnormal Studies | |
 |
|
4. Apical Four-Chamber View
| Probe position | Image |
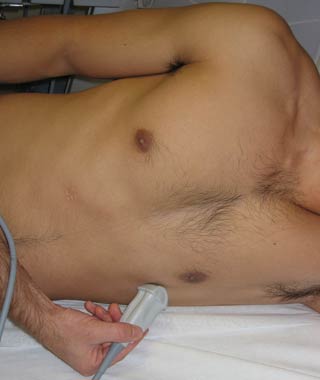 |
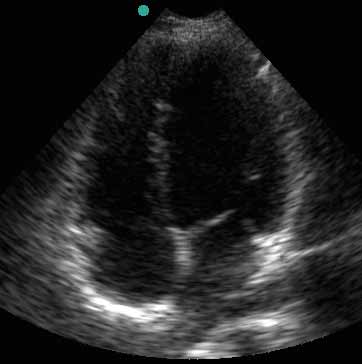 |
| Notes | |
|
|
| Abnormal Studies | |
 |
|
